I WANT
RELATED LINKS
I WANT
RELATED LINKS
RELATES LINKS
I WANT
RELATES LINKS
Services
Related Links

คำค้นหาที่แนะนำ
ผลการค้นหา "{{keyword}}" ไม่ปรากฎแต่อย่างใด
ข้อแนะนำในการค้นหา
- ตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของข้อความ
- ตรวจสอบภาษาที่ใช้ในการพิมพ์
- เปลี่ยนคำใหม่ กรณีไม่พบผลการค้นหา
Use and Management of Cookies
We use cookies and other similar technologies on our website to enhance your browsing experience. For more information, please visit our Cookies Notice.
- Personal Banking
- Stories & Tips
- Salary Man
- Urinary Tract Infection –A Danger Close to Office Workers
- Personal Banking
- ...
- Urinary Tract Infection –A Danger Close to Office Workers
Urinary Tract Infection –A Danger Close to Office Workers
14-07-2020
Written by Dr. Akanae Wongsawat
Urologist Surgeon at Phramongkutklao Hospital
Those who have to sit still and do their work for a long period of time, either at the workplace or at home. Those who always hold their urine when they are busy with their work or are on the flow of doing some activities and delay their time to go to the toilet. All these are the behaviors that can cause urinary tract infections. Despite not being fatal, the infection can cause annoyance and pain in life to the infected ones.
Knowing Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infection is an infection in the urinary tract caused by bacteria. According to the statistic, the infection is found more in women compared to men and is found mostly in people at the age of 20 – 50 years old, especially, in female office workers who are glued to their desk without moving anywhere. The reason that women have more risk of being infected is that the difference in the anatomy that women have shorter urinary tract than men’s. Thus, it is easier for bacteria around the entrance of the urinary tract to enter the urinary system. Besides, women’s urinary tract is exposed near the vagina and anus which increases the risk of them getting infected from bacteria.
The cause of UTI comes from many types of bacteria with around 75 – 95% caused by E. coli, which is commonly found around the anus region and can enter the human body through various means such as sexual intercourse, improper method of cleaning the anus region, usage of the tampon or urinary catheterization. Apart from that, UTI can be caused by other factors that is not bacteria, but it is rarely happened such as cystitis, drugs, sanitary products, pelvic radiation, or complications from other diseases.

Important factors that lead to UTI
- Holding urine for too long. This causes urine to remain in bladder for too long and bacteria in the urine to grow well.
- Urinate too frequently. This leads to forcing the urine out of the body and increases the contact with bacteria
- Improper sanitization of reproductive organs, especially women. If they clean in the wrong way, such as cleaning from the back to the front, there are more risks of getting the infection from the vagina and anus.
- Age. The change in hormones in women who stop menstruating causes estrogen to decrease. This makes the vagina and urinary tract less moist and, thus, causing the risk of infection to be higher.
- Diabetes. If patients with diabetes do not monitor their behaviors, they could easily get infected as their body originally have low immunity
- Little to no movement.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Drink less water
- Douche with antibiotics. This causes the good bacteria that fight infection to be removed and the body to be easily infected.
- Patients who need to take immunosuppressants.
- Using urinary catheter for too long.

Symptoms of UTI
The main symptoms are frequent urination and pain. It could be as frequent as every 1 – 2 hours or there is avoiding of small urine or stark pain that one would not want to urinate depending on how serious the condition is. It also has other symptoms such as:
- Unable to pass urine completely or there is leakage after urination.
- Pelvic pain when urinating completely. It could be extreme pain or intermittent or continuous pain.
- The urgency to urinate. Unable to hold that sometimes there is a leakage.
- There is blood dripping after urinate or there is a sign of blood in the urine.
- Cloudy urine.
- Urinate more than 2 times during the sleeping period.
In case of mild UTI or chronic UTI, the above-mentioned symptoms might not be significant that patients do not notice or patients might be already used to these symptoms.
Examine UTI
Patients are suggested to see the doctor, have their medical records asked and their body examined. During the examination, if there is pelvic pain, fever and there is white blood cells in the urine, the result would be UTI. Nevertheless, other causes that could lead or happen together with UTI have to be examined.
The diseases that could lead to UTI are:
- Urolithiasis (kidneys, renal pelvis, ureter, and bladder)· Urolithiasis (kidneys, renal pelvis, ureter, and bladder)
- Neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- Chronic urinary tract abnormalities since birth
- Cystocele
- Prolapsed uterus
- Urinary incontinence
- Overactive bladder
- Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM)
- Genitourinary cancer
In elderly men, they have to consider 3 important prostatic diseases which are benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, and prostate cancer.

Treatment for UTI
- Use suitable antibiotics. This includes the type of medication, intake amount, and duration.
- Administer medication such as painkillers, treatment for burning sensation, or difficulty in urination.
- Drink plenty of water about 2 – 5 liters per day (24 hours).
- Maintain normal body hygiene and after sexual activities.
- Follow up with urine check after taking medication (5 – 10 days).
Prevention of UTI
- Drink clean water at least 6 – 8 glasses.
- Do not hold urine.
- Initiate body movement.
- Maintain good hygiene.
- Do not use spray or deodorant on reproductive organs because it could cause irritation.
- Avoid bathing in a bathtub because it increases the risk of infection.
- If there is any abnormality, patients are advised to see a doctor for the appropriate treatment.
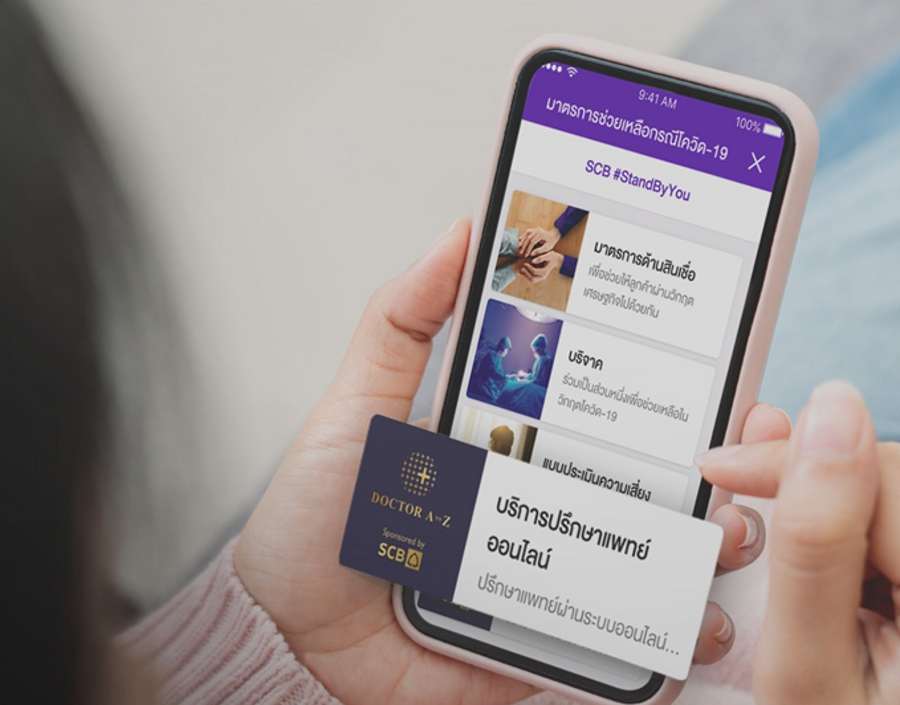
For those who have symptoms of UTI, but have got no time to see the doctor, SCB has cooperated with our partner to introduce online medical consultation. This allows you to gain access to basic medical consultation wherever you are. You can access it through SCB EASY App by clicking on “COVID – 19 Centre & Loan Relief Measures” and choose “Online Medical Consultation Service” (application service provided by Doctor A to Z sponsored by SCB).
For more information, go to https://www.scb.co.th/th/personal-banking/other-