I WANT
RELATED LINKS
I WANT
RELATED LINKS
RELATES LINKS
I WANT
RELATES LINKS
Services
Related Links
Use and Management of Cookies
We use cookies and other similar technologies on our website to enhance your browsing experience. For more information, please visit our Cookies Notice.
- Personal Banking
- Stories & Tips
- Protect My Family
- How should spouses plan their taxes to be the most economical?
- Personal Banking
- ...
- How should spouses plan their taxes to be the most economical?
How should spouses plan their taxes to be the most economical?
30-03-2020
Husband and wife should help plan the tax. Because good tax planning will help pay taxes correctly and economically. They will not have to be backward collected for taxes. And most importantly, they will not have to pay fines and extra money to heartbreak again
There are options for tax planning for spouses to pay taxes as follows
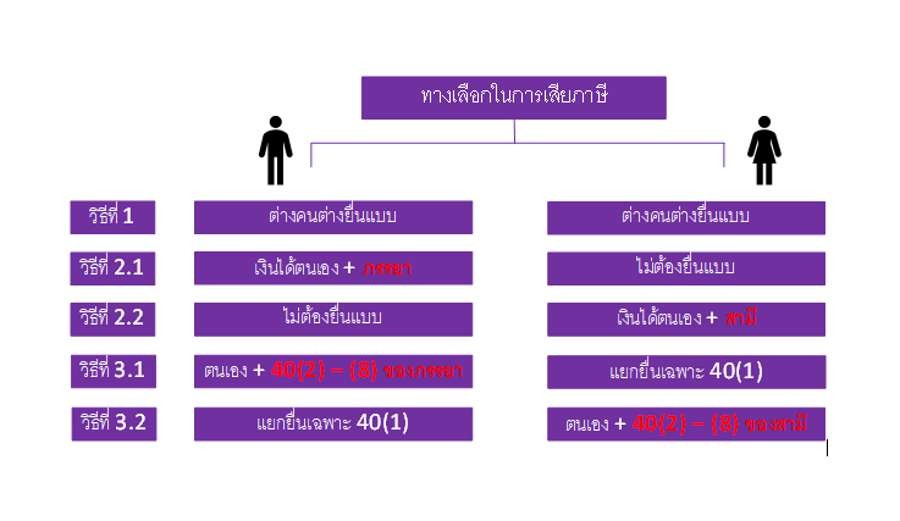
Note:
40 (1) Income from employment such as salary, bonus
40 (2) - (8) Other income which is not salary, such as commission fees, copyright fees, interest, dividends, property rentals Income from independent professions and other types of income
• Considering the options for filing personal income tax forms (Por Ngor Dor. 90/91), there are 3 methods as follows
Method 1 Separately submitting the Personal Income Tax Return form
Spouses registered with a marriage certificate can file tax return forms separately. Each can submit a form from their personal income - no need to combine income together. Moreover, each has its right to allowances and expense deductions separately.
This method is suitable for cases where both parties have an equal amount of income, paying taxes at a similar tax base rate. And with similar allowances for tax deductions. Causing each other to pay tax at an appropriate rate In addition, the separation will be convenient for both parties if you do not want the other party to interfere in managing their own personal money.
Method 2, including filing a return
This method is the combined income of both parties. Then bring to either party to be the form submission can be done in 2 ways which are
2.1 Combining the filing of returns under the husband's name means that the wife combines all of his income with the husband's total income. Then have the husband submit the form or
2.2 Including submitting the return statement on behalf of the wife is the husband's total income of his wife combined with the total income of the wife. Then having the wife submit the pattern
The collection of this form of filing Will be useful only when one party Have a very different income from the other party And those with lower incomes Cannot exercise full reduction rights Therefore, combine the income together and give the department more income than the filing form Makes it possible to include various tax deduction rights Of parties with low incomes That still does not fully utilize the rights To another party that has a higher tax burden

Method 3 Separately submit salary only as for other income Can be combined in the name of the other party can be done in 2 ways
3.1 Separate wives file tax forms for their own salaries as for other income Combined with the husband's income Then file a total tax push in the name of the husband or
3.2 Husbands separately file tax forms for their own salaries. As for other income Combined with the wife's income Then filed a combined tax in the name of his spouse
Other income such as interest, dividends, house rentals, employment payments, etc. This method is suitable for a spouse who has a high salary. And have income from other ways as well But deducting expenses and deductions in terms of full salary, legal rights Causing other additional incomes Except to not be able to deduct additional expenses Is also the additional income that causes the tax base to increase And have to pay more taxes Then can submit a salary-specific form And bring other income To be combined with the other party that has less income And still use the privilege of deduction And the cost is not yet full. It Will help save more taxes
Guidelines considered for exercising rights can be summarized as follows
Tax Deduction right | Separate filing | Total filing |
1. Person and spouse | 60,000 baht each | Combined not over 120,000 baht |
2. Children | 30,000 baht per person For the second child onwards, born since 2018, each person receives 60,000 baht. | Combined at 60,000 baht per 1 child For the 2nd child onwards who is born since 2018, each person is 120,000 baht per child. |
3. Parents | 30,000 baht per person Parents, spouses 30,000 baht per person | 30,000 baht per person Parents, spouses 30,000 baht per person |
4. Life insurance premiums | 100,000 baht per person If the spouse has no income, an additional deduction of the life insurance premium for 10,000 baht | Combined not over 200,000 baht (100,000 baht each)
|
5. Interest on home loan | Not exceeding 100,000 baht per year per person having income. The right will be with the person named in the contract as a borrower. On average, a deductible based on the number of borrowers. The reduction depends on the nature of the loan. | |
|
| |
We can see that spouses have different tax planning options and file tax forms and fairer Which to choose the right plan It depends on which type will give the most tax benefit. That is the most tax-saving and based on legal validity.
Reference: The Revenue Code Section 47 and the Revenue Department's explanation regarding the guidelines for personal income tax collection from husband and wife (Version 2), 2012.
บทความโดย : Nipapan Poonsathianrasap CFP® Independent Financial Advisor, Writer and Lecturer
